What is an Industrial Videoscope?
An industrial videoscope, also known as a borescope or inspection camera, is a sophisticated optical instrument widely used in various industries for non-destructive testing and inspection purposes. This advanced tool allows professionals to visually inspect and assess the condition of hard-to-reach or inaccessible areas, such as pipes, machinery, engines, and other components, without the need for disassembly.
Key Components:
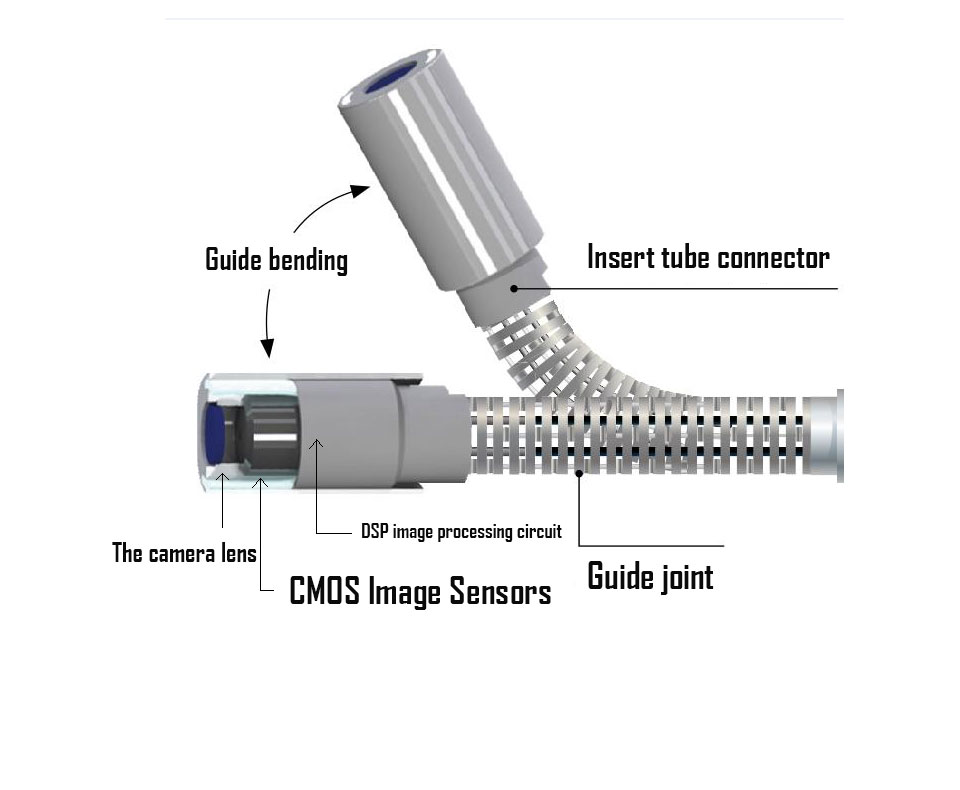
- Flexible Insertion Tube: The videoscope consists of a flexible insertion tube that is maneuverable and allows access to confined spaces. This tube is usually made of durable materials, such as tungsten or braided stainless steel, to withstand challenging industrial environments.
- High-Resolution Camera: The tip of the insertion tube is equipped with a high-resolution camera, often equipped with LED lights for illumination. The camera captures real-time images or videos, providing a clear view of the inspection area.
- Articulation System: Many industrial videoscopes are designed with an articulation system, enabling the user to remotely control the direction of the camera tip. This feature allows for a more comprehensive inspection of complex structures.
- Light Source: Integrated light sources illuminate the inspection area, ensuring visibility in dark or poorly lit environments. This is crucial for capturing detailed images and identifying potential issues.
- Control Unit: The control unit is a handheld device or console that allows the user to operate and control the videoscope. It typically includes a display screen, joystick, buttons, and knobs for easy navigation and adjustment of settings.
Applications:
- Aerospace Industry: Videoscopes are used to inspect aircraft engines, turbine blades, and other critical components without disassembling them, ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace equipment.
- Automotive Maintenance: In the automotive industry, videoscopes are employed to inspect engine cylinders, exhaust systems, and other internal components, aiding in preventative maintenance and diagnostics.
- Oil and Gas Inspection: Videoscopes play a crucial role in inspecting pipelines, wellbores, and other oil and gas infrastructure, helping to identify corrosion, leaks, and other potential issues.
- Manufacturing Quality Control: Industrial videoscopes are used for quality control in manufacturing processes, allowing inspectors to examine the internal structure of products, welds, and assemblies.
- Power Generation: The power generation sector uses videoscopes to inspect turbines, boilers, and heat exchangers, ensuring the efficiency and reliability of power plants.
Benefits:
- Cost-Efficiency: Avoiding the need for disassembly reduces downtime and labor costs associated with inspections.
- Precision and Accuracy: High-resolution imaging provides detailed and accurate visual data, aiding in the identification of potential issues.
- Safety: Videoscopes enable inspections of hazardous or difficult-to-reach areas without exposing personnel to unnecessary risks.
- Preventative Maintenance: Early detection of issues through regular inspections allows for proactive maintenance, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures.
In conclusion, industrial videoscopes have become indispensable tools across various industries, revolutionizing the way inspections are conducted and contributing to enhanced safety, efficiency, and reliability in industrial operations.